Osteopathy
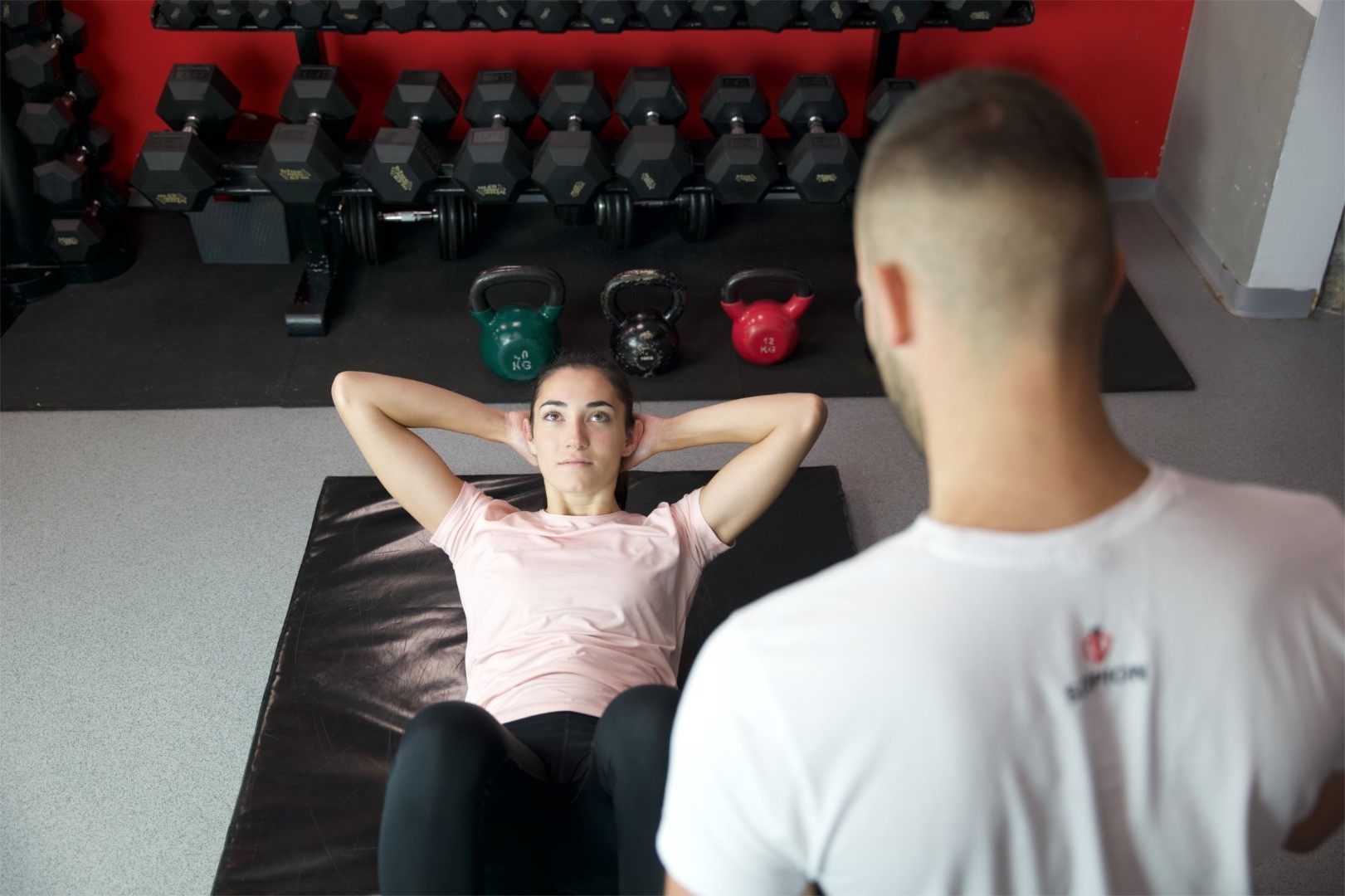
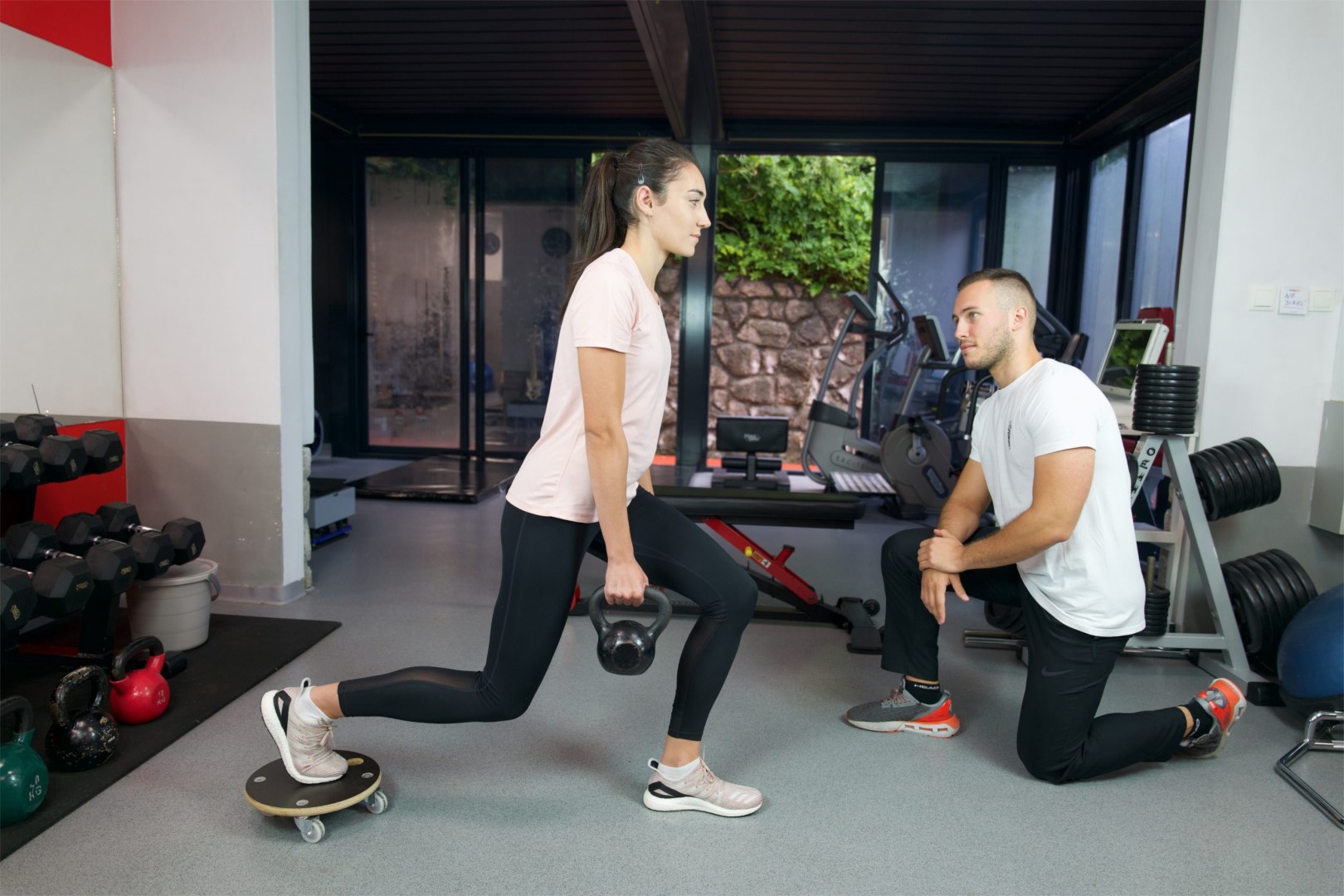
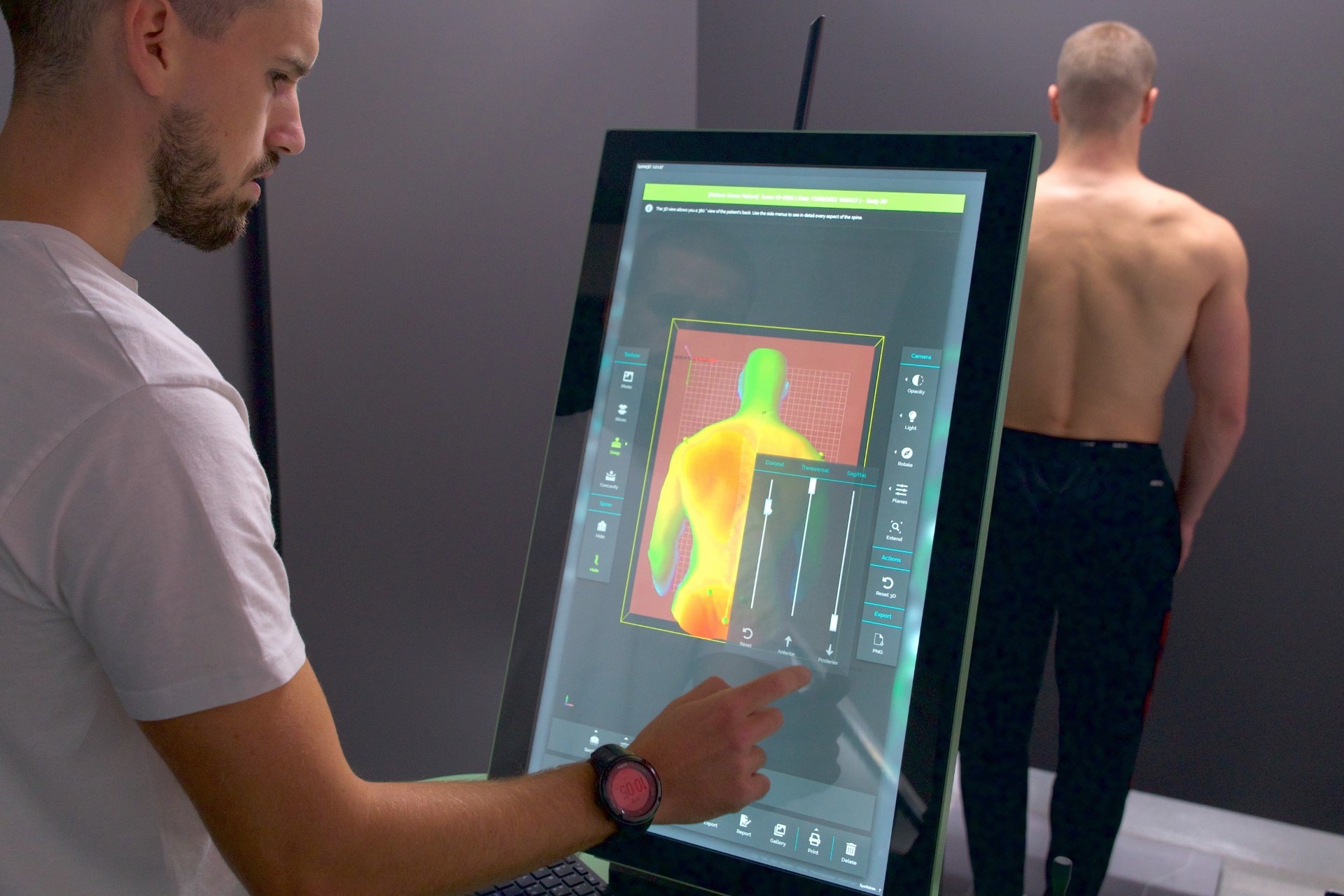
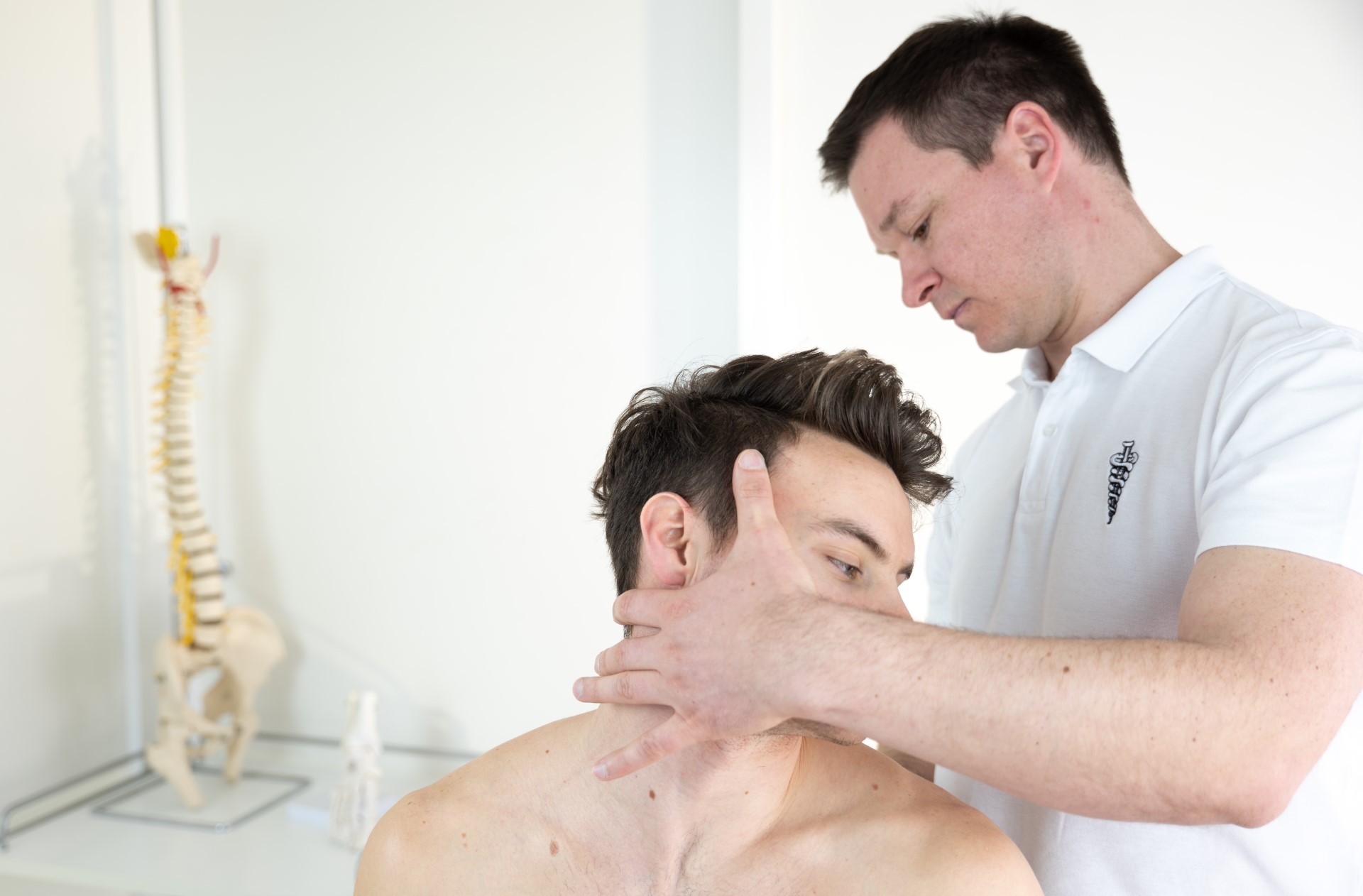
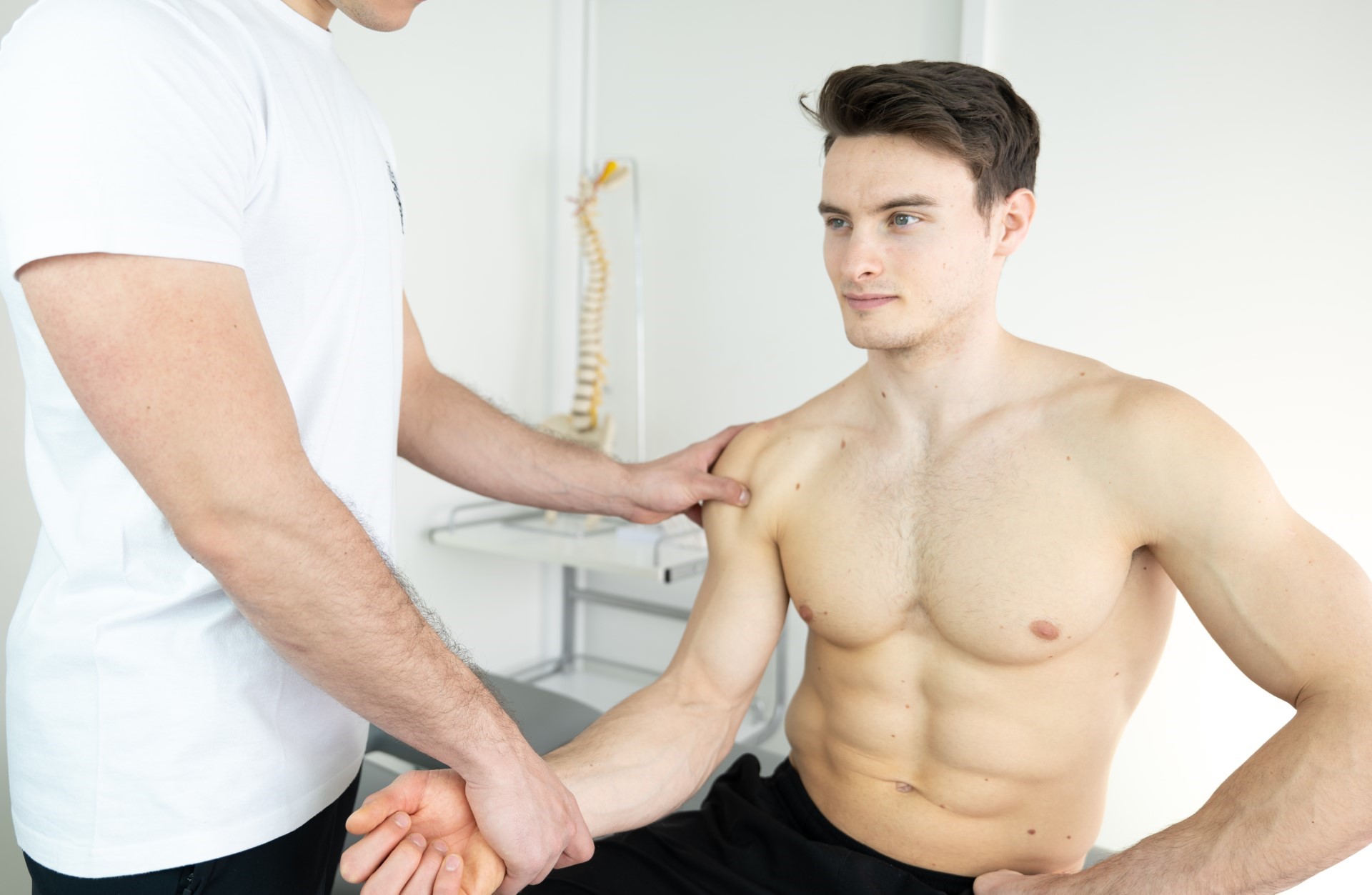
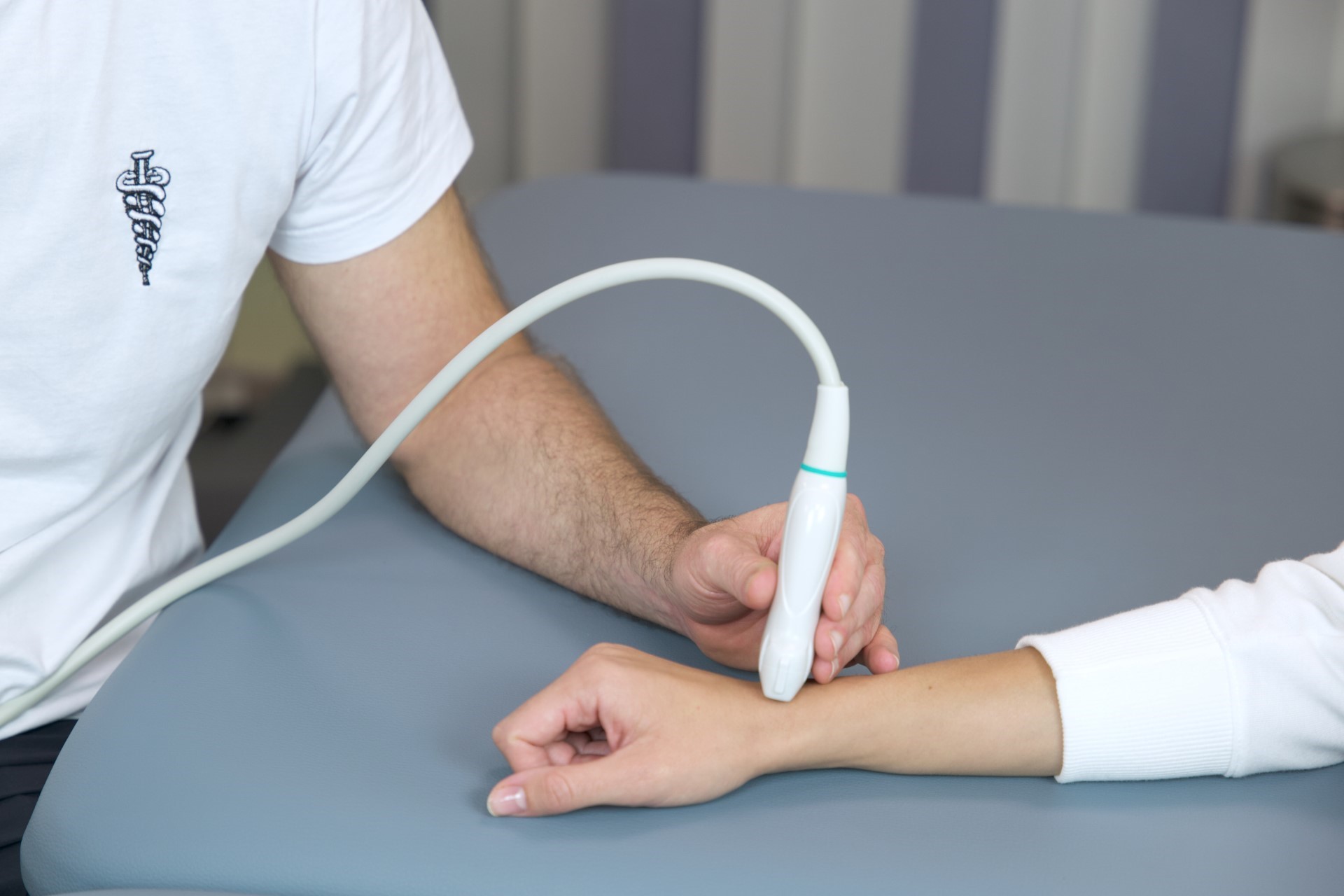
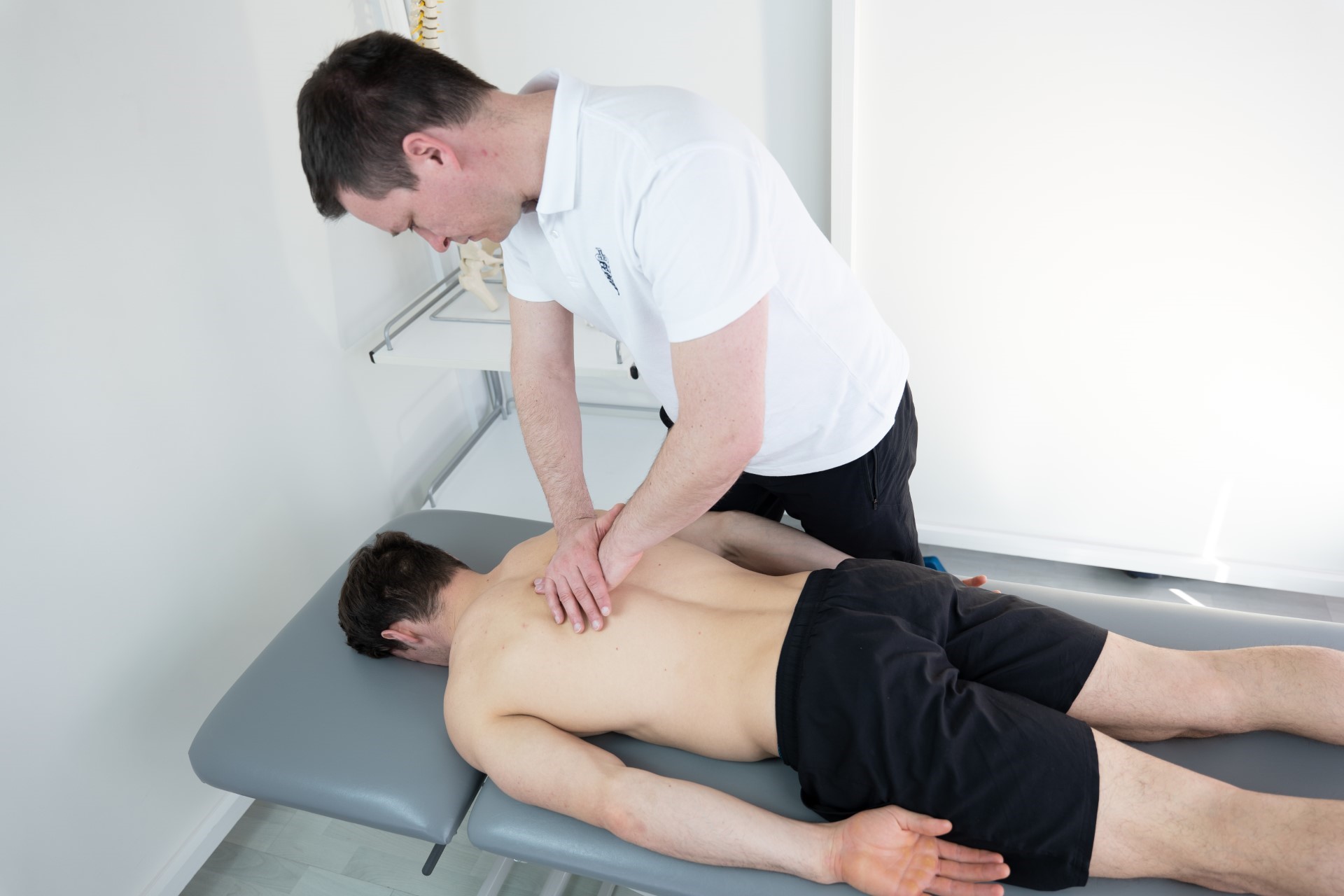
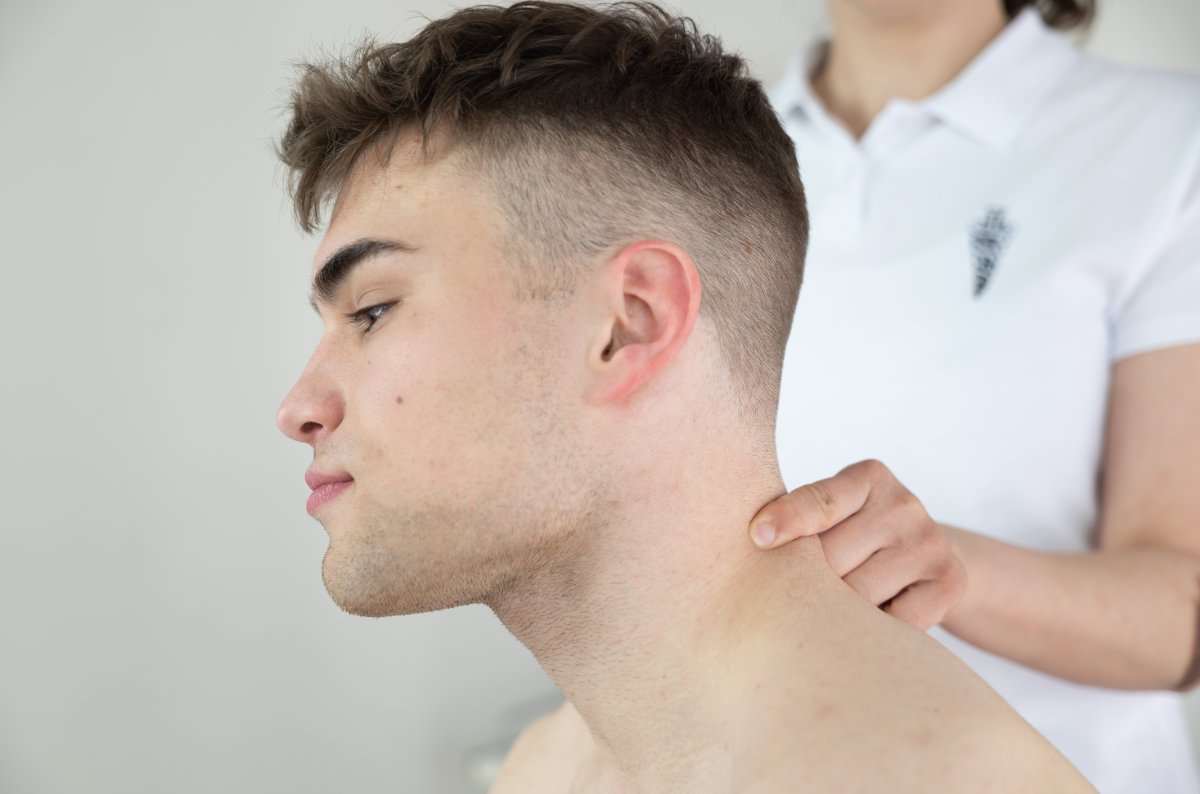
Osteopathy is a specialized form of manual medicine that seeks out blockages within the body and addresses the root causes of these blockages. It views the body holistically as an interconnected system that functions as a whole. Palpation is the primary tool in osteopathy, used to diagnose and treat somatic dysfunction within the body. Somatic dysfunction is defined as impaired and altered function of specific components of the body, including myofascial, bony, and joint structures in relation to nervous and vascular structures. Therefore, it is crucial to detect the site of somatic dysfunction through a detailed medical history and comprehensive clinical examination of the patient, which may not always align with the location where the patient experiences symptoms. These dysfunctions compromise the tissue’s adaptive capabilities to withstand external stressors such as certain functional movements, unfavorable postural positions, traumas, excessive physical work, and more.
Osteopathy operates on clear principles applied in clinical practice, promoting health rather than curing disease.
The father of osteopathy, Andrew Taylor Still, viewed the body as an integrated whole and emphasized osteopathic principles based on the synchronized dynamic connection of all components within the body. Every part of the body is interconnected from the surface of the skin to each cell, from the macroscopic to the microscopic level, and fascia plays a crucial role in maintaining the complex relationship between the structure and function of the body, fluid dynamics, matrix biology, and mechanobiology. Fascia acts as a unifying element within the body, facilitating movement and maintaining the integrity of various body parts. When fascia is under continuous tension, mobility and function may be compromised.
Osteopathy is a science, art, skill, and philosophy that views the body holistically, considering the musculoskeletal, visceral, neurological, and cranial systems, employing a wide range of techniques that are very gentle and painless. Osteopaths possess extensive knowledge of functional and clinical anatomy to conduct precise global evaluations of patients and identify the site of local or primary somatic dysfunction within specific organ systems.
Osteopathy addresses a wide spectrum of diseases and complaints, including musculoskeletal disorders, visceral disorders, neurological disorders, and cranial disorders. In addition to common mechanical issues of the musculoskeletal system, such as neck pain, back pain, joint pain, and muscle pain, osteopathy can be beneficial for headaches, dizziness, tinnitus, some respiratory issues, digestive disorders, gynecological conditions, and disturbances in growth and development phases.
PLACE AN ORDER OR SEND INQUIRY
Our expert team is here for you!